
Constructors in JS
Constructors in JavaScript are a special type of function that is used to create objects. They are used to initialize the properties of an object when it is created. Constructors are defined using the function keyword followed by the name of the constructor function. The constructor function is called when the object is created using the new keyword.
What is a Constructor in JavaScript?
A constructor is a special function used to create and initialize objects.It’s like a blueprint for making similar objects with the same structure but different values.
By convention, constructor function names start with a capital letter.
When you use the new keyword, JavaScript:
Creates a new empty object.
Sets the new object’s prototype to the constructor’s prototype.
Calls the constructor function with this bound to the new object.
Returns the new object (unless the constructor explicitly returns something else).
Syntax of a Constructor Function
A class is a blueprint or a template that defines the properties and methods of an object. It is a way to define a set of attributes and methods that can be used to create objects. Classes are the foundation of OOP's, and they are used to model real-world objects and their interactions.
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
We then create objects like this:
const person1 = new Person("Alice", 25);
const person2 = new Person("Bob", 30);
Key Differences
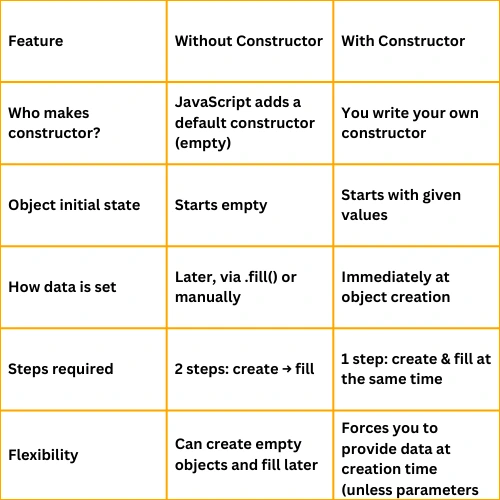
Example with Constructor and without Constructor
class CarDefault {
start() {
console.log(`Car started: Brand = ${this.brand || "Unknown"}, Color = ${this.color || "Unknown"}`);
}
}
let car1 = new CarDefault();
car1.brand = "Toyota";
car1.color = "Red";
car1.start(); // Car started: Brand = Toyota, Color = Red
// Class with custom constructor
class CarCustom {
constructor(brand, color) {
this.brand = brand;
this.color = color;
}
start() {
console.log(`Car started: Brand = ${this.brand}, Color = ${this.color}`);
}
}
let car2 = new CarCustom("Honda", "Blue"); // custom constructor sets data immediately
car2.start(); // Car started: Brand = Honda, Color = Blue
What This Shows
CarDefault: JavaScript gives a default constructor.
CarDefault: You create an empty object and set properties later.
CarCustom: You define your own constructor.
CarCustom: Properties are set right at creation — ready to use immediately.